
Fake Transaction Hash Scam Explained: How Scammers Prove Payments That Never Happened
The fake transaction hash scam is a deceptive crypto fraud where scammers provide victims with a fabricated or misleading transaction ID to falsely prove that a payment was sent. This scam targets users who rely on screenshots, copied hashes, or unfamiliar blockchain explorers instead of verifying transactions correctly.
It is commonly used in peer-to-peer trades, fake refunds, fake withdrawals, and follow-up scams after earlier losses.
What Is a Fake Transaction Hash Scam?
A fake transaction hash scam occurs when a scammer claims they have sent crypto and backs it up with:
- A fake transaction ID
- A manipulated screenshot
- A link to a fake blockchain explorer
- A real hash from a different transaction
The goal is to convince the victim that payment has already been made, so they release funds, send crypto, or stop questioning delays.
How the Fake Transaction Hash Scam Works
This scam relies on information asymmetry — scammers know the victim does not fully understand how to verify blockchain transactions.
Step 1: The Payment Claim
The scammer claims:
- A withdrawal was processed
- A refund was sent
- A payment is “pending on the blockchain”
They insist the delay is normal.
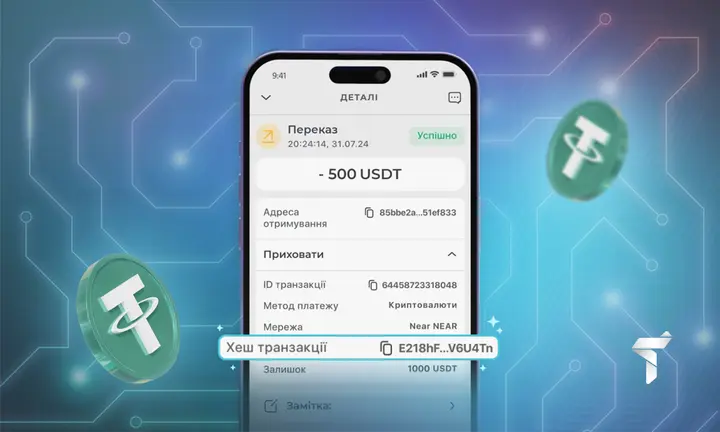
Step 2: Providing a Fake or Misleading Hash
The victim is given:
- A random-looking transaction hash
- A screenshot of a transaction
- A link to a blockchain explorer clone
- A real hash from another wallet
To most users, it looks legitimate.
Step 3: Pressure and Reassurance
The scammer adds pressure:
- “Check the hash, it’s already sent”
- “The blockchain is slow today”
- “You just need to wait for confirmations”
This discourages further questioning.
Step 4: The Realization
Eventually, the victim realizes:
- No funds ever arrived
- The hash doesn’t belong to them
- The explorer link was fake
- The transaction was unrelated
By then, the scammer has disappeared or escalated the scam.
Common Variations of the Scam
Fake Refund Scam
Victims are told their money was refunded and shown a transaction hash as proof, even though no refund exists.
Fake Withdrawal Scam
Users of fake platforms are told withdrawals were sent, but “pending,” supported by a fake hash.
P2P Trade Scam
In peer-to-peer deals, scammers claim they sent crypto and push the victim to release assets.
Recovery Follow-Up Scam
After an earlier scam, victims are told recovered funds were sent and shown a fake transaction.
Why This Scam Is So Effective
The fake transaction hash scam works because:
- Transaction hashes look complex and technical
- Most users don’t know how to verify ownership
- Screenshots feel convincing
- Blockchain confirmation delays are believable
- Victims don’t want to seem inexperienced
Scammers exploit hesitation and uncertainty.
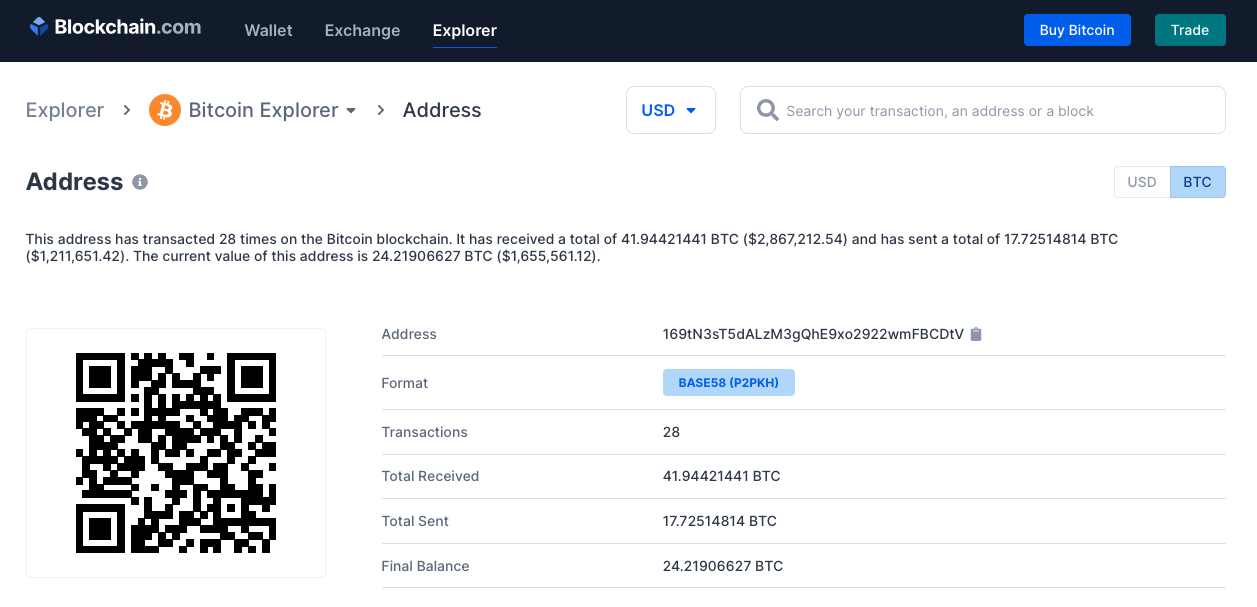
How to Tell a Fake Transaction Hash from a Real One
A real transaction must:
- Appear on a legitimate blockchain explorer
- Show the correct receiving address
- Match the exact amount
- Be visible without logging in
- Be searchable independently (not just via a link)
If you can’t independently find it, it likely doesn’t exist.
Red Flags Most Victims Miss
- Being told to rely on screenshots
- Being given a link instead of a public explorer name
- Hash not showing your wallet address
- Claims of “internal processing” after a hash is shared
- Requests to wait before verifying independently
Any attempt to stop verification is a warning sign.
Why Funds Are Never “Pending” Without Evidence
On public blockchains:
- A transaction is either broadcast or it isn’t
- Pending transactions are visible immediately
- There is no such thing as a hidden transaction
- Confirmations do not hide transfers
If nothing appears publicly, nothing was sent.
Who Is Most Targeted
This scam often targets:
- P2P traders
- Crypto freelancers
- NFT sellers
- Scam victims expecting refunds
- New crypto users
However, experienced users can fall for it during rushed transactions.
How to Protect Yourself
You can reduce risk by:
- Verifying transactions on official explorers
- Never trusting screenshots alone
- Checking receiving addresses carefully
- Waiting for confirmations before releasing assets
- Ignoring pressure tactics
Verification should always be done independently.
Final Thoughts
The fake transaction hash scam shows that not all crypto fraud involves hacking or smart contracts. Sometimes, a scammer only needs a convincing string of characters and confidence.
In crypto, proof matters. If a transaction cannot be independently verified on the blockchain, it does not exist — no matter how professional the explanation sounds.
Understanding this scam can prevent costly mistakes and stop fraud before it escalates.